Fluoride
Durango, CO
Another tool for prevention is our regular fluoride treatments. We recommend that all children have this throughout their teenage years. If you aren't on public water, this is particularly important for preventing cavities. Statistically, if your child has a fluoride treatment in our dental office, their risk for getting cavities decreases by thirty percent. This is significant when you are considering the overall health and wellbeing of your child. With that in mind, we use whatever tools are at our disposal to ensure that your child is as healthy and as comfortable as possible both now and as they age. If you live in the Durango area, we invite you to schedule a dental exam by calling (970) 259-1646.
What is fluoride?
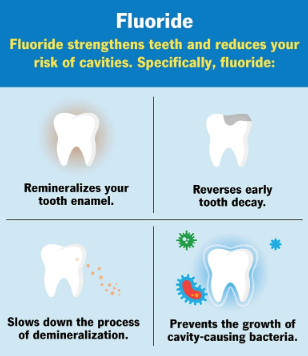
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral found in many foods and water. In dentistry, fluoride is used to strengthen teeth and reduce the risk of cavities.
What does fluoride do?
Every day, your enamel (the protective outer layer of your tooth) gains and loses minerals. You lose minerals when acids – formed from bacteria, plaque and sugars in your mouth – attack your enamel, demineralizing your teeth. You gain minerals – like fluoride, calcium and phosphate – when you consume food and water that contain these minerals, this process is remineralization.
Tooth decay is a result of too much demineralization without enough remineralization. Dental fluoride helps prevent tooth decay by making your enamel more resistant to acid attacks. It can also reverse early decay.
Types of fluoride used in dentistry
Many foods and water contain fluoride. You can also purchase fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash. You can buy low-strength fluoride mouthwash over the counter. Stronger concentrations in liquid or tablet form need a healthcare provider’s prescription.
How is fluoride applied?
At Durango Dentistry, our dentist or dental hygienist uses a fluoride varnish that is painted directly on your teeth, a process that takes about five minutes. It is non-invasive and has no pain. You can eat and drink right away after application. However, it is recommended to avoid sticky and crunchy food for about 4 hours. Also wait until bedtime to brush your teeth so you don’t brush the varnish off right away.
How often should I have fluoride treatments?
Many people benefit from fluoride treatment every 6 months, however it depends on your unique oral health needs. If you’re prone to cavities, you might benefit from more frequent treatments.
At what age is fluoride intake most important?
Infants and children between the ages of 6 months and 16 years need an appropriate amount of fluoride. Developing teeth benefit from fluoride just as much as teeth that have already grown in.
The ADA, American Dental Association, recommends infants and young children use breast milk, ready-to-feed formula or prepared formula mixed with fluoride-free water. These recommendations are to guard again enamel fluorosis (explained below in Why do I have spots on my teeth?).
For young children, the ADA recommends:
· Using a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste at each brushing.
· Spitting our rather than swallowing the toothpaste. It’s best to avoid flavored toothpaste as children are more likely to swallow.
· Not allowing children under age 6 to use fluoride mouth rinses unless recommended by a dentist or other healthcare provider.
· Not giving fluoride-containing dietary supplements to children under 6 months of age.
Can adults benefit from fluoride?
Yes, adults can benefit from fluoride, too. In addition to fighting cavities, fluoride also reduces tooth sensitivity. Some conditions can especially benefit from fluoride:
Dry Mouth – A common side effect of some health conditions and medications. Salvia (spit) helps wash away food particles and bacteria. Slower salvia production may make you more prone to oral health issues like gum disease and cavities.
Gum Disease – Which exposes your teeth and gums to bacteria and increase your risk of tooth decay.
Tooth Decay – If you have a history of tooth decay or more prone to cavities.
Crowns, Bridges, Braces, Partial Dentures – Can increase your risk of cavities, especially around the bracket of braces or where the crown meets your tooth.
Is fluoride dangerous?
While fluoride can be harmful in large quantities, it’s difficult to reach toxic levels due to the low amount of fluoride in over-the-counter products like toothpaste and mouth washes. A toxic dosage level is based on a person’s weight.
Why do I have spots on my teeth?
The most common side effect of fluoride is fluorosis. This may occur when excess levels of fluoride are ingested during tooth development, usually in children under the age of 6. It does not occur from professional fluoride treatments performed by a dentist. Fluorosis varies in appearance from white striations to stained pitting of enamel.
Fluorosis most often results from consuming naturally occurring fluoride, like that found in well water. You can get your well water tested to find out how much fluoride is in your water. Contact your local health department or water supplier.
In the United States, about 74% of people with public water supplies have adequate levels of fluoride in their water.
You can’t brush fluorosis away, but if you have concerns call Durango Dentistry (970)259-1646 to schedule a consult with a dentist to determine best course of action, from teeth whitening, dental bonding to dental veneers.
Definition of Dental Terminology
Dental Caries
Dental caries is also known as cavities and result from a lack of proper oral hygiene leaving plaque that forms tiny holes in the teeth.
Dental Sealants
Dental sealants are a solution of plastic material that we apply to the crown of the tooth to protect the areas within the ridges of teeth from infection.
Dental Prophylaxis
A dental prophylaxis is a thorough cleaning procedure that involves preventing the spread or continued growth of periodontal disease and gingivitis.
Dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the oral cavity.
Etchant
Etchant is a gentle acid to treat the surface of a specific tooth to help the filling material stick to the tooth.
Occlusion
Occlusion describes the mandibular and maxillary rows of teeth meeting when the patient bites down. If a patient does not have a healthy bite, they are struggling with malocclusion.
Overjet
An overjet is a bite orientation that results from the maxillary central incisors (top center teeth) protruding over the mandibular central incisors (bottom front teeth); this may also be known as “buck teeth” by patients.
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Pregnancy gingivitis is gingivitis that results from the common change in hormones during pregnancy that increases blood flow to the gum tissue, increasing sensitivity, irritability and swelling in the gums.